Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C and
C and  He
HeAkeo, Kiyoshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Akeo, Yoko*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 80, 2015/03
It is known that superoxide dismutases (SOD) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the dismutation of superoxide into oxygen and hydrogen peroxide. Ionizing radiation is known to induce oxidative stress through generation of reactive oxygen species resulting in imbalance of the pro-oxidant and antioxidant in the cells, which is suggested to culminate in cell death. Therefore, we measured the activity of SOD in human RE cells exposed to the He- and C-ion beam. The cells collected at 0, 4, 8, and 24 hr after irradiation were extracted by adding the SOD assay buffer to the pellets, and lysed by several cycles of freezing and thawing. The activity of SOD was measured using a modification of the luminol assay. SOD activity decreased according to duration time after irradiation of He-ion, however, in case of C-ion, it increased at 24 hr after irradiation. The result suggested that that there were the differences of the effects by irradiation on SOD activity between He- and C-ion.
Kitabatake, Satomi*; Ushiroda, Tota*; Hirayama, Ryoichi*; Furusawa, Yoshiya*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Okahata, Yoshio*; Ito, Atsushi*
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 86, 2015/03
Biological effects of high-LET radiation could be understood in terms of the ion track structure. Therefore the evaluation of the contribution of both core and penumbra regions to biological effects is an important issue for the study of high-LET effects. In the present study, we developed a protocol to make a uniform DNA sheet with insoluble nature in aqueous solution, and explored the applicability to the detection of 8-OHdG distributions after heavy-ion irradiation. Water-insoluble DNA sheet was irradiated with proton and neon ion beams at JAEA-Takasaki. After irradiation DNA samples were incubated with an 8-OHdG antibody followed by with a second antibody containing a fluorescence probe. The preliminary results indicated that upon ion irradiation randomly distributed dot-like fluorescence was observed, suggesting that these dots may be from incident ions.
 Cu
Cu Oy under magnetic field
Oy under magnetic fieldIshikawa, Norito; Sueyoshi, T.*; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Fujiyoshi, T.*; Miyahara, K.*; Kisu, T.*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 284-288(Part1), p.873 - 874, 2000/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.15(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
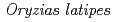 )
)Asaka, Tomomi*; Hashimoto, Chika*; Ito, Kazusa*; Yasuda, Takako*; Nagata, Kento*; Nishimaki, Toshiyuki*; Katsumura, Takafumi*; Ota, Hiroki*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
no journal, ,
It is thought that the irradiation to the particular area of the individual could induce the irradiation impact to the outside of the irradiated area in addition to the irradiated region. In this study, we established the procedures to conduct carbon ion irradiation on adult Medaka, which can irradiate only either dorsal or ventral side of the fish, using the broad-beam irradiation system of JAEA-Takasaki. The irradiated fish were examined heart rate before the fixation. Thereafter, the systemic alteration was evaluated by serial cross sections of the whole body of the fish. Tissues at the irradiated side were seriously injured that corresponded to the range of the beam. However, secondary gill lamella showed the characteristic edema in either the ventral or dorsal irradiated fish unless the gill located at ventral, suggesting the systemic irradiation effect. There was no alteration in the heart rate after the irradiation suggesting no severe effects in blood flow in this condition.
Oda, Shoji*; Yasuda, Takako*; Hibi, Yusuke*; Asaka, Tomomi*; Ikeda, Hiroko; Muto, Yasuko*; Yokota, Yuichiro; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Suzuki, Michiyo; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a new irradiation protocol for tissue specific irradiation to living embryo and adult medaka, 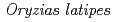 . In the study, a testis of p53 knockout fish were irradiated with multi-shots of microbeam. Less numbers of testis-ova were induced in the in p53- lacking testis 1 week after the irradiation compared to whole body irradiated testis. Specific irradiation of microbeam onto the right (or left) lobe of the optic tectum in medaka embryos of 2 days post fertilization ectopically induced apoptotic cells in the body trunk and the tail in addition to the irradiated position. The systemic effects as endocrine system, autonomic nervous system and immunity reactions occur in adult medaka and these results suggested that the systemic effects might be functional even in developing embryos.
. In the study, a testis of p53 knockout fish were irradiated with multi-shots of microbeam. Less numbers of testis-ova were induced in the in p53- lacking testis 1 week after the irradiation compared to whole body irradiated testis. Specific irradiation of microbeam onto the right (or left) lobe of the optic tectum in medaka embryos of 2 days post fertilization ectopically induced apoptotic cells in the body trunk and the tail in addition to the irradiated position. The systemic effects as endocrine system, autonomic nervous system and immunity reactions occur in adult medaka and these results suggested that the systemic effects might be functional even in developing embryos.
Asaka, Tomomi*; Ito, Kazusa*; Hashimoto, Chika*; Yasuda, Takako*; Nagata, Kento*; Nishimaki, Toshiyuki*; Katsumura, Takafumi*; Ota, Hiroki*; Suzuki, Michiyo; Funayama, Tomoo; et al.
no journal, ,
Radiotherapy has been widely used in cancer target. It is thought that the irradiation to the particular area of the individual could induce the irradiation impact to the nearby and distant tissues of the irradiated area in addition to the irradiated region. However, it is still difficult to analyze influences to the whole body using mice because of its big body size. Medaka, 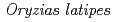 , is small enough to examine the acute somatic effects induced in all tissues at the cellular levels. In this study, we developed a method to conduct local irradiation on adult medaka using low energy carbon-ion beam in TIARA, JAEA-Takasaki. The irradiated fish were measured the heart rate to evaluate the impact to the heart, chemically fixed, serially sectioned and Hematoxylin/eosin stained. The results suggested that there would be the systemic effects by local irradiation in addition to the effects in the irradiated region, which is probably caused by immune system though blood.
, is small enough to examine the acute somatic effects induced in all tissues at the cellular levels. In this study, we developed a method to conduct local irradiation on adult medaka using low energy carbon-ion beam in TIARA, JAEA-Takasaki. The irradiated fish were measured the heart rate to evaluate the impact to the heart, chemically fixed, serially sectioned and Hematoxylin/eosin stained. The results suggested that there would be the systemic effects by local irradiation in addition to the effects in the irradiated region, which is probably caused by immune system though blood.